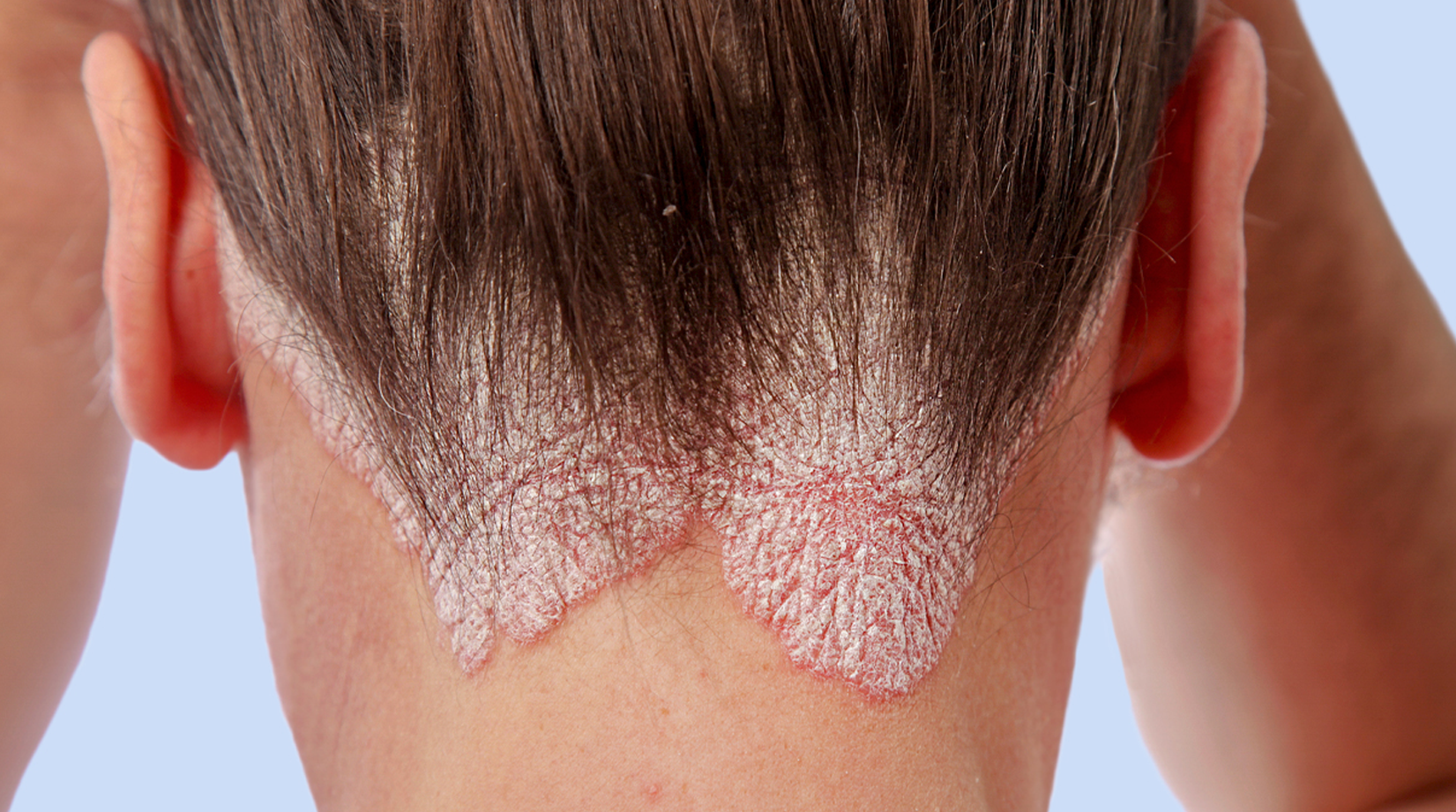
What is it?
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease, which is common and chronic. It can cause dry, red, scaly patches and flakes on the skin. When psoriasis occurs, the skin cells multiply ten times faster than normal. It causes a build-up of dead skin cells on the surface of the skin that do not have the time to fall off.
Symptoms
- Red, inflamed patches of skin
- Plaques on the red patches
- Dry skin that cracks and bleeds
- Soreness
- Itching and burning sensations
- Painful and swollen joints
Causes
- Immune system:
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition where the white blood cells, known as T cells, mistakenly attack the skin cells, which speed up the production of skin cell causing new skin cells to develop too quickly. - Genetics
- HIV
- Obesity
- Stress
Types of Psoriasis
- Plaque Psoriasis is the type of Psoriasis that causes dry, raised, red skin lesions covered with silvery scales. The plaques formed might be itchy or painful. They can occur anywhere on the patient’s body, including the genitals and the soft tissue inside the mouth.
- Nail Psoriasis is the type that can affect the fingernails and toenails, causing pitting, abnormal nail growth, and discoloration. In this type, the nails will loosen up and get separated from the nail bed.
- Guttate psoriasis is usually triggered by a bacterial infection such as the strep throat. The small, water-drop-shaped, and scaling lesions present on the trunk, arms, legs, and scalp of the patient is a mark for this type of psoriasis.
- Inverse Psoriasis is a type of psoriasis that affects the skin present in
|
|
|
|
This type of psoriasis can also occur as smooth patches of red and inflamed skin that can worsen with friction and sweating. It is usually triggered by fungal infections.
- Pustular Psoriasis generally develops quickly, with pus-filled blisters appearing just hours after the patient’s skin becomes red and tender. These blisters might come and go frequently. Patients with this type of psoriasis might ecperience fever, chills, severe itching, and diarrhea.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis can cover the patient’s entire body with a red, peeling rash that can itch or burn intensely.
- Psoriatic Arthritis is the condition where, in addition to an inflamed and scaly skin, psoriatic arthritis can cause swollen and painful joints that are typical of arthritis. It can cause stiffness and progressive joint damage that in the most serious cases might lead to permanent deformity.
Treatment
- Topical treatments: include creams and ointments that are applied directly to the skin. This will help in the reduction of cases varying from mild to moderate psoriasis.
- Systemic Medications: People with moderate to severe psoriasis may need to use oral or injected medications. Many of these medications have severe side effects. Doctors usually prescribe them for a short period of time.
- Light Therapy is a thereapy that uses ultraviolet (UV) or natural light to treat the psoriasis. This light kills the overactive white blood cells that attack the healthy skin cells and cause rapid cell growth.
Lifestyle Changes
Some of the lifestyle changes that can help ease the symptoms of psoriasis are:
- Lose weight
- Eat a heart-healthy diet
- Avoid trigger foods (red meat, refined sugar, processed foods, dairy products)
- Consider taking vitamins


